Who dated Charles Maurice de Talleyrand-Périgord?
Maria Teresa Poniatowska dated Charles Maurice de Talleyrand-Périgord from ? until ?. The age gap was 6 years, 9 months and 15 days.
Germaine de Staël dated Charles Maurice de Talleyrand-Périgord from ? until ?. The age gap was 12 years, 2 months and 9 days.
Dorothea von Medem dated Charles Maurice de Talleyrand-Périgord from ? until ?. The age gap was 6 years, 11 months and 21 days.
Princess Dorothea of Courland dated Charles Maurice de Talleyrand-Périgord from ? until ?. The age gap was 39 years, 6 months and 19 days.
Adélaïde Filleul, Marquise de Souza-Botelho dated Charles Maurice de Talleyrand-Périgord from ? until ?. The age gap was 7 years, 3 months and 12 days.
Mademoiselle Luzy dated Charles Maurice de Talleyrand-Périgord from until . The age gap was 6 years, 8 months and 7 days.
Charles Maurice de Talleyrand-Périgord

Description in English not found, we only have a description in English:
Charles-Maurice de Talleyrand-Périgord (; French: [ʃaʁl mɔʁis də tal(ɛ)ʁɑ̃ peʁiɡɔʁ, moʁ-]; 2 February 1754 – 17 May 1838), 1st Prince of Benevento, then Prince of Talleyrand, was a French secularized clergyman, statesman, and leading diplomat. After studying theology, he became Agent-General of the Clergy in 1780. In 1789, just before the French Revolution, he became Bishop of Autun. He worked at the highest levels of successive French governments, most commonly as foreign minister or in some other diplomatic capacity. He served as the French Diplomat in the Congress of Vienna. His career spanned the regimes of Louis XVI, the years of the French Revolution, Napoleon, Louis XVIII, Charles X, and Louis Philippe I. Those Talleyrand served often distrusted him but found him extremely useful. The name "Talleyrand" has become a byword for crafty and cynical diplomacy.
Talleyrand was Napoleon's chief diplomat during the years when French military victories brought one European state after another under French hegemony. Most of the time, he worked for peace so as to consolidate France's gains. He succeeded in obtaining peace with Austria through the 1801 Treaty of Lunéville and with Britain in the 1802 Treaty of Amiens. He could not prevent the renewal of war in 1803 but by 1805 he opposed his emperor's renewed wars against Austria, Prussia, and Russia. He resigned as foreign minister in August 1807, but retained the trust of Napoleon. He conspired to undermine the emperor's plans through secret dealings with Tsar Alexander I of Russia and the Austrian minister Klemens von Metternich. Talleyrand sought a negotiated secure peace so as to perpetuate the gains of the French Revolution. Napoleon rejected peace; when he fell in 1814, Talleyrand supported the Bourbon Restoration decided by the Allies. He played a major role at the Congress of Vienna in 1814–1815, where he negotiated a favorable settlement for France and played a role in unwinding the Napoleonic Wars.
Talleyrand polarizes opinion. Some regard him as one of the most versatile, skilled, and influential diplomats in European history, while others believe that he was a traitor, betraying in turn the ancien régime, the French Revolution, and Napoleon.
Maria Teresa Poniatowska

Maria Teresa Antonina Józefina z Poniatowskich Tyszkiewiczowa (ur. 28 listopada 1760 w Wiedniu, zm. 2 listopada 1834 w Tours we Francji) – dama Krzyża Orderowego zakonu maltańskiego.
Urodziła się jako pierwsze dziecko generała-lejtnanta w służbie austriackiej i czeskiej Andrzeja Poniatowskiego (późniejszego księcia Korony Czeskiej) i hrabianki Theresy Kinsky von Wchinitz und Tettau. Do chrztu trzymała ją cesarzowa Maria Teresa. Jej bratem był książę Józef Poniatowski.
Gdy miała trzynaście lat na gruźlicę zmarł jej ojciec, co spowodowało, że wziął ją pod kuratelę brat jej ojca król Stanisław August Poniatowski. Mieszkając w Wiedniu, zachorowała w szesnastym roku życia, w wyniku czego usunięto jej gałkę oczną. Gdy miała osiemnaście lat, zgodnie z wolą Stanisława Augusta, wydano ją za mąż za Wincentego Tyszkiewicza herbu Leliwa, hrabiego na Łohojsku i Świsłoczy, referendarza wielkiego litewskiego. Małżeństwo nie było udane, dlatego wkrótce opuściła męża.
Przez 30 lat, od 1807, blisko z nią związany był francuski minister spraw zagranicznych Francji Charles-Maurice de Talleyrand-Périgord.
Read more...Charles Maurice de Talleyrand-Périgord

Germaine de Staël

Anne Louise Germaine de Staël-Holstein (French: [an lwiz ʒɛʁmɛn də stal ɔlstajn]; née Necker; 22 April 1766 – 14 July 1817), commonly known as Madame de Staël ( də-STAHL; French: [madam də stal]), was a prominent philosopher, woman of letters, and political theorist in both Parisian and Genevan intellectual circles. She was the daughter of banker and French finance minister Jacques Necker and Suzanne Curchod, a respected salonist and writer. Throughout her life, she held a moderate stance during the tumultuous periods of the French Revolution and the Napoleonic era, persisting until the time of the French Restoration.
Her presence at critical events such as the Estates General of 1789 and the 1789 Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen underscored her engagement in the political discourse of her time. However, Madame de Staël faced exile for extended periods: initially during the Reign of Terror and subsequently due to personal persecution by Napoleon. She claimed to have discerned the tyrannical nature and ambitions of his rule ahead of many others.
During her exile, she fostered the Coppet group, a network that spanned across Europe, positioning herself at its heart. Her literary works, emphasizing individuality and passion, left an enduring imprint on European intellectual thought. De Staël's repeated championing of Romanticism contributed significantly to its widespread recognition.
Within her work, de Staël not only advocates for the necessity of public expression but also sounds cautionary notes about its potential hazards.
Read more...Charles Maurice de Talleyrand-Périgord

Dorothea von Medem
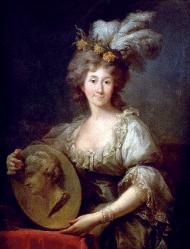
Countess Anna Charlotte Dorothea von Medem (3 February 1761 – 20 August 1821) was born a Gräfin (Countess) of the noble Baltic German Medem family and later became Duchess of Courland. Popularly known as Dorothea of Courland after her marriage to Peter von Biron, the last Duke of Courland, she hosted an aristocratic salon in Berlin and performed various diplomatic duties on behalf of her estranged husband. She would spend the rest of her life in her estate in Löbichgau, where she would invite and host many important political and cultural figures of the time and make many acquaintances, ranging from Goethe over Napoleon I of France to Talleyrand, the latter of whom she was reportedly very close.
Read more...Charles Maurice de Talleyrand-Périgord

Princess Dorothea of Courland

Dorothea von Biron, Princess of Courland, Duchess of Dino, Duchess of Talleyrand and Duchess of Sagan, known as Dorothée de Courlande or Dorothée de Dino (21 August 1793 – 19 September 1862), was a Baltic German noblewoman, and the ruling Duchess of Sagan between 1845 and 1862. Her mother was Dorothea von Medem, Duchess of Courland, and although her mother's husband, Duke Peter von Biron, acknowledged her as his own, her true father may have been the Polish statesman Count Aleksander Batowski. For a long time, she accompanied the French statesman Charles Maurice de Talleyrand-Périgord; she was the separated wife of his nephew, Edmond de Talleyrand-Périgord.
Read more...Charles Maurice de Talleyrand-Périgord

Adélaïde Filleul, Marquise de Souza-Botelho

Adélaïde-Émilie (sometimes Émilie-Adélaïde) Filleul, Marquise de Souza-Botelho (14 May 1761 – 19 April 1836) was a French writer.
Read more...Charles Maurice de Talleyrand-Périgord

Mademoiselle Luzy

Dorothée Dorinville, stage name Mademoiselle Luzy (1747–1830), was a French stage actress.
She was engaged at the Comédie-Française in 1764. She became a Sociétaires of the Comédie-Française in 1764. She retired in 1781.
She was most known as a soubrette, but also performed tragedy, and acted as a singer and dancer. She was described as a serious and ambitious stage artist, and was a part of the movement that wished to introduce realistic stage costumes. She was imprisoned in 1771 after having broken the censure laws in a play by Imbert.
Read more...